4.2.1. Exposure to credit risk
Pursuant to Rule Thirteen in the Solvency Circular concerning the capital requirements for credit risk, exposure is understood to be any asset item and all items included in the Group’s memorandum accounts involving credit risk and not deducted from the Group’s eligible capital. Accordingly, inclusion is made mainly of customer lending items, with their corresponding undrawn balances, letters of credit and guarantees, debt securities and capital instruments, cash and deposits in central banks and credit institutions, assets purchased or sold under a repurchase agreement (asset and liability repos), financial derivatives and fixed assets.
Below is a presentation of the original exposure and the allowances for losses under the advanced measurement and standardized approaches as of December 31, 2012 and 2011. In accordance with section one of Rule Twenty-eight of the Solvency Circular, only the exposure net of allowances is presented for those exposures calculated under the standardized approach.
In the comparison between the two exercises there can be seen to be a growth in credit risk exposures calculated by the standard method. This is basically due to the entry of Unnim into the Group's portfolio and the increased lending activity in the Group's subsidiaries in Latin America:
- The original exposure to central and regional government and other public-sector authorities falls due to lower volumes in repos.
- Exposure to companies increases due to the incorporation of the Unnim loan book into the Group's portfolio and the increased activity in this segment in the Latin American subsidiaries of Mexico, Venezuela and Chile.
- In the case of retail exposure, the growth in the original exposure is once more explained by Unnim, with €3 billion, and the growth of business in the Latin American subsidiaries.
- The increased exposure in the category of real-estate collateralized loans is due to a combination of two effects: the Unnim portfolio (€10.5 billion) and a fall by a transfer of part of the portfolio of Spain to internal models.
- The increased exposure to default corresponds basically to Unnim.
With respect to exposure by credit risk calculated using internal models, the categories of Institutions and Corporates is reduced by the deleveraging in the Spanish market mentioned above.
The increase in the retail categories is due basically to the transfer to internal consumer, credit card and mortgage models.
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
|
|
|
Exposure after applying conversion factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category of exposure | Original exposure (1) | Provisions (2) | Exposure net of provisions (3) | On-balance-sheet exposure after mitigation techniques | Off-balance-sheet exposure after mitigation techniques | Fully adjusted value of the exposure | Average CCF | EAD |
| Central governments and central banks | 108,378 | -193 | 108,185 | 97,958 | 3,197 | 101,155 | 73% | 100,299 |
| Regional governments and local authorities | 9,361 | 0 | 9,361 | 6,775 | 255 | 7,030 | 43% | 6,884 |
| Public-sector institutions and other public entities | 3,096 | -1 | 3,095 | 2,990 | 1,365 | 4,355 | 40% | 3,539 |
| Multilateral development banks | 187 | 0 | 187 | 67 | 133 | 200 | 12% | 83 |
| International organizations | 34 | 0 | 34 | 34 | 0 | 34 | 1% | 34 |
| Institutions | 18,855 | -12 | 18,843 | 12,799 | 5,937 | 18,736 | 16% | 13,761 |
| Corporates | 98,219 | -1,686 | 96,533 | 56,930 | 33,486 | 90,417 | 31% | 67,341 |
| Retail | 55,783 | -195 | 55,589 | 38,875 | 13,778 | 52,653 | 11% | 40,345 |
| Collateralized with real-estate property | 54,193 | -169 | 54,024 | 51,164 | 45 | 51,209 | 23% | 51,174 |
| Default status | 11,489 | -2,581 | 8,908 | 8,014 | 55 | 8,069 | 61% | 8,048 |
| High risk | 1,596 | -73 | 1,523 | 1,327 | 37 | 1,364 | 22% | 1,335 |
| Guaranteed bonds | 503 | 0 | 503 | 503 | 0 | 503 | 0% | 503 |
| Short-term to institutions and corporates | 656 | 0 | 656 | 645 | 0 | 645 | 0% | 645 |
| Mutual funds | 53 | 0 | 53 | 24 | 28 | 52 | 100% | 52 |
| Other exposures | 23,081 | -7 | 23,074 | 27,350 | 489 | 27,838 | 31% | 27,502 |
| TOTAL STANDARDIZED APPROACH | 385,483 | -4,916 | 380,567 | 305,457 | 58,804 | 364,261 | - | 321,544 |
| Central governments and central banks | 1,092 | -2 |
|
1,947 | 859 | 2,805 | 51% | 2,382 |
| Institutions | 77,129 | -53 |
|
71,686 | 5,882 | 77,568 | 60% | 75,187 |
| Corporates | 133,851 | -6,284 |
|
75,084 | 56,583 | 131,668 | 55% | 106,014 |
| Retail | 94,022 | -1,501 |
|
83,895 | 10,159 | 94,054 | 27% | 86,653 |
| Secured by real-estate collateral | 70,970 | -445 |
|
70,590 | 380 | 70,970 | 10% | 70,630 |
| Qualifying revolving retail | 16,415 | -622 |
|
6,742 | 9,674 | 16,415 | 28% | 9,427 |
| Other retail assets | 6,636 | -434 |
|
6,563 | 105 | 6,668 | 32% | 6,596 |
| TOTAL ADVANCED MEASUREMENT APPROACH | 306,095 | -7,841 |
|
232,611 | 73,483 | 306,095 | - | 270,237 |
| SUBTOTAL CREDIT RISK (securitizations and equity positions not included) | 691,577 | -12,757 |
|
538,069 | 132,287 | 670,356 | - | 591,781 |
| Securitized positions | 9,409 | -177 |
|
9,361 | 0 | 9,361 | 0 | 9,277 |
| Standardized Approach | 6,685 | -47 | 6,637 | 6,637 | - | 6,637 | 0 | 6,553 |
| Advanced Measurement Approach | 2,724 | -130 |
|
2,724 | - | 2,724 | 0 | 2,724 |
| Equity | 6,234 | -225 |
|
5,744 | - | 5,744 | 0 | 6,234 |
| Simple Method | 947 | -66 |
|
947 | - | 947 | 0 | 947 |
| Non-trading equity instruments in sufficiently diversified portfolios | 694 | -64 |
|
694 | - | 694 | 0 | 694 |
| Exchange-traded equity instruments | 253 | -2 |
|
253 | - | 253 | 0 | 253 |
| PD/LGD Method | 4,798 | 0 |
|
4,798 | - | 4,798 | 0% | 4,798 |
| Internal Models | 489 | -159 |
|
0 | - | 0 | 0% | 489 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK | 707,220 | -13,160 |
|
553,174 | 132,287 | 685,462 | - | 607,292 |
(2) It includes provisions for the impairment of assets (financial and non-financial) and other valuation adjustments, with the exception of the generic provision included in the capital base as more Additional Capital, as per Rule Eight in the Solvency Circular.
(3) Exposures are adjusted solely by provisions in the case of exposures by the Standardized Approach.
2011
(Million euros)
|
|
|
|
|
Exposure after applying conversion factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category of exposure | Original exposure (1) | Provisions (2) | Exposure net of provisions (3) | On-balance-sheet exposure after mitigation techniques | Off-balance-sheet exposure after mitigation techniques | Fully adjusted value of the exposure | Average CCF | EAD |
| Central governments and central banks | 112,419 | -11 | 112,408 | 79,807 | 3,532 | 83,339 | 70% | 82,274 |
| Regional governments and local authorities | 12,128 | 0 | 12,128 | 7,117 | 3,061 | 10,178 | 63% | 9,044 |
| Public-sector institutions and other public entities | 4,115 | 0 | 4,114 | 3,218 | 807 | 4,025 | 49% | 3,613 |
| Multilateral development banks | 39 | - | 39 | 34 | 22 | 55 | 0% | 34 |
| International organizations | 12 | 0 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0% | 12 |
| Institutions | 16,293 | -24 | 16,269 | 12,278 | 4,198 | 16,476 | 18% | 13,014 |
| Corporates | 92,579 | -1,576 | 91,003 | 57,107 | 30,261 | 87,368 | 41% | 69,518 |
| Retail | 48,151 | -287 | 47,864 | 33,445 | 13,312 | 46,757 | 16% | 35,618 |
| Collateralized with real-estate property | 45,300 | -111 | 45,189 | 43,680 | 211 | 43,891 | 49% | 43,784 |
| Default status | 8,632 | -1,175 | 7,457 | 7,395 | 7 | 7,402 | 59% | 7,399 |
| High risk | 1,874 | -42 | 1,833 | 1,754 | 55 | 1,809 | 48% | 1,781 |
| Guaranteed bonds | 78 | 0 | 78 | 78 | 0 | 78 | 0% | 78 |
| Short-term to institutions and corporates | 895 | 0 | 895 | 895 | 0 | 895 | 0% | 895 |
| Mutual funds | 216 | 0 | 216 | 164 | 52 | 216 | 99% | 215 |
| Other exposures | 20,522 | -12 | 20,510 | 26,208 | 788 | 26,997 | 70% | 26,763 |
| TOTAL STANDARDIZED APPROACH | 363,252 | -3,237 | 360,015 | 273,192 | 56,306 | 329,497 | - | 294,042 |
| Central governments and central banks | 1,909 | -4 |
|
2,755 | 993 | 3,748 | 48% | 3,228 |
| Institutions | 98,320 | -44 |
|
91,098 | 7,674 | 98,772 | 56% | 95,412 |
| Corporates | 156,313 | -3,356 |
|
91,360 | 62,661 | 154,021 | 52% | 123,761 |
| Retail | 82,430 | -1,059 |
|
76,550 | 5,880 | 82,430 | 33% | 78,512 |
| Secured by real-estate collateral | 68,859 | -392 |
|
68,643 | 217 | 68,859 | 12% | 68,668 |
| Qualifying revolving retail | 10,374 | -536 |
|
4,711 | 5,663 | 10,374 | 34% | 6,648 |
| Other retail assets | 3,196 | -131 |
|
3,196 | 0 | 3,196 | 100% | 3,196 |
| TOTAL ADVANCED MEASUREMENT APPROACH | 338,972 | -4,464 |
|
261,763 | 77,208 | 338,972 | - | 300,913 |
| SUBTOTAL CREDIT RISK (securitizations and equity positions not included) | 702,224 | -7,701 |
|
534,955 | 133,514 | 668,469 | - | 594,954 |
| Securitized positions | 8,396 | -255 |
|
8,264 | 0 | 8,264 | 0 | 8,264 |
| Standardized Approach | 6,351 | -131 | 6,220 | 6,220 | - | 6,220 | 0 | 6,220 |
| Advanced Measurement Approach | 2,045 | -123 |
|
2,045 | - | 2,045 | 0 | 2,045 |
| Equity | 6,426 | -433 |
|
5,946 | - | 5,946 | 0 | 6,426 |
| Simple Method | 1,216 | -314 |
|
1,216 | - | 1,216 | 0 | 1,216 |
| Non-trading equity instruments in sufficiently diversified portfolios | 610 | -27 |
|
610 | - | 610 | 0 | 610 |
| Exchange-traded equity instruments | 606 | -287 |
|
606 | - | 606 | 0 | 606 |
| PD/LGD Method | 4,730 | -2 |
|
4,730 | - | 4,730 | 0% | 4,730 |
| Internal Models | 480 | -117 |
|
0 | - | 0 | 0% | 480 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK | 717,045 | -8,389 |
|
549,165 | 133,514 | 682,679 | - | 609,644 |
(2) It includes provisions for the impairment of assets (financial and non-financial) and other valuation adjustments, with the exception of the generic provision included in the capital base as more Additional Capital, as per Rule Eight in the Solvency Circular.
(3) Exposures are adjusted solely by provisions in the case of exposures by the Standardized Approach.
4.2.2. Average value of the exposures throughout 2012 and 2011.
(Million euros)
|
|
Original average exposure for the period | |
|---|---|---|
| Category of exposure | 2012 | 2011 |
| Central governments and central banks | 107,063 | 105,229 |
| Regional governments and local authorities | 9,034 | 8,811 |
| Public-sector institutions and other public entities | 2,967 | 4,162 |
| Multilateral development banks | 82 | 45 |
| International organizations | 396 | 12 |
| Institutions | 19,396 | 16,483 |
| Corporates | 96,500 | 84,920 |
| Retail | 55,665 | 46,872 |
| Collateralized with real-estate property | 49,547 | 46,236 |
| Default status | 9,978 | 8,714 |
| High risk | 1,749 | 1,967 |
| Guaranteed bonds | 361 | 34 |
| Short-term to institutions and corporates | 757 | 694 |
| Mutual funds | 140 | 138 |
| Other exposures | 21,852 | 17,870 |
| TOTAL STANDARDIZED APPROACH | 375,485 | 342,188 |
| Central governments and central banks | 1,515 | 3,059 |
| Institutions | 91,627 | 96,325 |
| Corporates | 143,931 | 157,715 |
| Retail | 92,077 | 82,726 |
| Secured by real-estate collateral | 70,933 | 69,324 |
| Qualifying revolving retail | 15,119 | 10,109 |
| Other retail assets | 6,024 | 3,294 |
| TOTAL ADVANCED MEASUREMENT APPROACH | 329,149 | 339,826 |
| SUBTOTAL CREDIT RISK (securitizations and equity positions not included) | 704,633 | 682,014 |
| Securitized positions | 9,073 | 8,234 |
| Standardized Approach | 6,603 | 6,063 |
| Advanced Measurement Approach | 2,469 | 2,171 |
| Equity | 6,069 | 6,875 |
| Simple Method | 1,068 | 1,294 |
| Non-trading equity instruments in sufficiently diversified portfolios | 649 | 787 |
| Exchange-traded equity instruments | 419 | 507 |
| PD/LGD Method | 4,526 | 5,054 |
| Internal Models | 475 | 527 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK | 719,776 | 697,122 |
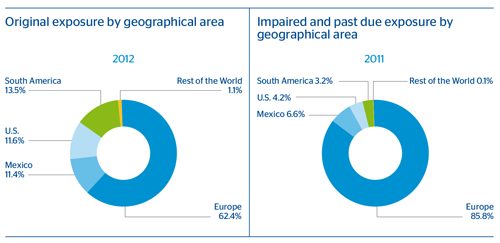
4.2.3. Distribution by geographical area
The following chart present the distribution by significant geographic areas of the original exposure by country pursuant to the obligor's country. The breakdown includes exposure under the standardized and advanced measurement approaches, without including positions in equity.
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
Original exposure by geographical area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category of exposure | Total | Europe | Mexico | U.S. | South America | Rest of the World |
| Central governments and central | 108,378 | 72,769 | 12,857 | 5,732 | 17,000 | 20 |
| banks | 9,361 | 1,752 | 6,387 | 968 | 189 | 65 |
| Regional governments and local | 3,096 | 1,337 | 0 | 269 | 1,490 | 0 |
| authorities | 18,855 | 9,019 | 2,522 | 89 | 7,127 | 98 |
| Public-sector institutions and other | 98,219 | 20,409 | 18,244 | 35,990 | 23,111 | 465 |
| public entities | 55,783 | 19,075 | 7,020 | 6,214 | 23,450 | 25 |
| Institutions | 54,193 | 19,618 | 10,795 | 12,379 | 11,397 | 4 |
| Corporates | 6,685 | 1,824 | 82 | 4,779 | 0 | 0 |
| Retail | 37,598 | 19,896 | 7,847 | 2,821 | 6,916 | 117 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK BY THE STANDARDIZED APPROACH | 392,168 | 165,698 | 65,756 | 69,240 | 90,679 | 794 |
| Central governments and central banks | 1,092 | 40 | 3 | 218 | 552 | 280 |
| Institutions | 77,129 | 71,030 | 19 | 3,827 | 310 | 1,944 |
| Corporates | 133,851 | 116,677 | 1,260 | 8,203 | 3,130 | 4,581 |
| Retail | 94,022 | 81,271 | 12,604 | 18 | 40 | 89 |
| Securitized positions | 2,724 | 2,674 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 38 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK BY THE ADVANCED MEASUREMENT APPROACH | 308,819 | 271,692 | 13,885 | 12,279 | 4,032 | 6,931 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK | 700,986 | 437,390 | 79,641 | 81,520 | 94,711 | 7,725 |
The next table shows the distribution by geographical area of the book balances of the non-performing and impaired exposures of financial and non-financial assets and for contingent liabilities.
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
Total | Europe | Mexico | U.S. and Puerto Rico | South America | Rest of the World |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-performing and impaired exposures | 19,824 | 17,017 | 1,315 | 834 | 634 | 25 |
The next table shows the distribution by geographical area of the book balances of the allowances for financial asset losses and for contingent liabilities.
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
Total | Europe | Mexico | U.S. and Puerto Rico | South America | Rest of the World |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-performing and impaired exposures | 14,917 | 10,766 | 1,683 | 924 | 1,505 | 39 |
4.2.4. Distribution by sector
The following table shows the distribution by economic sector (standardized and advanced measurement approaches) of the original exposure. The breakdown does not include positions in equity.
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
Original exposure by sector | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category of exposure | Total | EECC, Insurance and Financial Brokerage | Public sector | Agriculture | Industry | Construction | Commercial | Individuals | Other sectors |
| Central governments and central banks | 108,378 |
|
15.5% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Regional governments and local authorities | 9,361 |
|
1.3% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Public-sector institutions and other public entities | 3,096 |
|
0.4% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Institutions | 18,855 | 2.7% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Corporates | 98,219 | 0.9% |
|
0.5% | 1.8% | 1.2% | 5.9% |
|
2.5% |
| Retail | 55,783 | 0.1% |
|
0.1% | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.9% | 5.2% | 0.9% |
| Collateralized with real-estate property | 54,193 |
|
|
0.1% | 0.1% | 0.9% | 0.4% | 5.0% | 0.3% |
| Securitized positions | 6,685 | 0.3% | 0.5% |
|
|
|
0.2% |
|
|
| Other exposures | 37,598 | 0.4% |
|
0.1% | 0.2% | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.8% | 2.9% |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK BY THE STANDARDIZED APPROACH | 392,168 | 4.3% | 17.8% | 0.7% | 2.5% | 2.7% | 7.6% | 10.9% | 6.6% |
| Central governments and central banks | 1,092 |
|
0.2% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Institutions | 77,129 | 7.4% | 3.6% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Corporates | 133,851 | 2.1% | 0.6% | 0.1% | 6.8% | 2.0% | 2.1% | 0.0% | 3.3% |
| Retail | 94,022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.4% |
|
| Securitized positions | 2,724 | 0.4% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK BY THE ADVANCED MEASUREMENT APPROACH | 308,819 | 9.9% | 4.3% | 0.1% | 6.8% | 2.0% | 2.1% | 13.4% | 3.4% |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK | 700,986 | 14.2% | 22.2% | 0.8% | 9.3% | 4.8% | 9.7% | 24.3% | 9.9% |
The following table shows the distribution by counterparty of the book balances of the non-performing and impaired exposures of financial assets and contingent liabilities.
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
Total | EECC, Insurance and Financial Brokerage | Public sector | Corporates | Retail | Other sectors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-performing and impaired exposures | 19,824 | 1.8% | 1.0% | 62.2% | 26.3% | 8.7% |
The next table shows the distribution by counterparty of the book balances of allowances for financial asset losses and for contingent exposures:
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
Total | EECC, Insurance and Financial Brokerage | Public sector | Corporates | Retail | Other sectors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific value adjustments | 9,830 | 1.8% | 0.8% | 68.5% | 21.7% | 7.2% |
| Generic provisions | 5,047 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Country risk | 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Value adjustments and provisions, total | 14,917 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.2.5. Distribution by residual maturity
The following table presents the distribution of original exposure by residual maturity, broken down by category of exposure under the standardized and advanced measurement approaches:
2012
(Million euros)
|
|
|
Original exposure by residual maturity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category of exposure | Total | Less than 1 year | Between 1 and 5 years | Over 5 years |
| Central governments and central banks | 108,378 | 68,441 | 25,664 | 14,273 |
| Regional governments and local authorities | 9,361 | 2,163 | 1,385 | 5,813 |
| Public-sector institutions and other public entities | 3,096 | 1,674 | 880 | 542 |
| Institutions | 18,855 | 9,625 | 5,263 | 3,967 |
| Corporates | 98,219 | 37,817 | 36,889 | 23,513 |
| Retail | 55,783 | 21,417 | 20,565 | 13,802 |
| Collateralized with real-estate property | 54,193 | 5,588 | 14,870 | 33,735 |
| Securitized positions | 6,685 | 133 | 1,303 | 5,249 |
| Other exposures (1) | 37,598 | 19,067 | 8,968 | 9,562 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK BY THE STANDARDIZED APPROACH | 392,167 | 165,925 | 115,786 | 110,455 |
| Central governments and central banks | 1,092 | 174 | 311 | 607 |
| Institutions | 77,129 | 37,894 | 19,022 | 20,213 |
| Corporates | 133,851 | 61,948 | 38,989 | 32,914 |
| Retail | 94,022 | 696 | 4,224 | 89,102 |
| Securitized positions | 2,724 | 63 | 490 | 2,171 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK BY THE ADVANCED MEASUREMENT APPROACH | 308,819 | 100,775 | 63,036 | 145,007 |
| TOTAL CREDIT RISK (2) | 700,986 | 266,701 | 178,822 | 255,463 |
(2) Equity Positions are not included.
4.2.6. Value adjustments for impairment losses and allowances for contingent risks and commitments
The following table presents the movement recorded in the years 2012 and 2011 in the allowance for impairment losses of financial assets on the balance sheet and for contingent liabilities and commitments, including country risk, generic and specific allowances.2012
(Million euros)
| Item | Financial assets value adjustments and provisions | Provisions for Contingent Liabilities and Commitments | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| BALANCE AT START OF 2010 | 10,039 | 291 | 10,330 |
| Increase in impairment charged to income | 10,643 | 105 | 10,747 |
| Decrease in impairment credited to income | -2,333 | -44 | -2,377 |
| Institutions acquired by the Group during the year | 2,067 | 5 | 2,072 |
| Institutions disposed of during the year | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Transfers to written-off loans | -4,143 | 0 | -4,143 |
| Exchange differences and other transactions | -1,471 | -16 | -1,487 |
| BALANCE AT END OF YEAR 2011 | 14,801 | 341 | 15,142 |
| For impaired portfolio | 9,889 | 166 | 10,055 |
| For current non-impaired portfolio | 4,912 | 175 | 5,087 |
2011
(Million euros)| Item | Financial assets value adjustments and provisions | Provisions for Contingent Liabilities and Commitments | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| BALANCE AT START OF 2011 | 10,093 | 264 | 10,357 |
| Increase in impairment charged to income | 6,103 | 17 | 6,120 |
| Decrease in impairment credited to income | -1,551 | -24 | -1,574 |
| Institutions acquired by the Group during the year | 305 | 12 | 317 |
| Institutions disposed of during the year | 0 | 0 | - |
| Transfers to written-off loans | -4,114 | 0 | -4,114 |
| Exchange differences and other transactions | -797 | 22 | -775 |
| BALANCE AT END OF YEAR 2012 | 10,039 | 291 | 10,330 |
| For impaired portfolio | 6,903 | 135 | 7,038 |
| For current non-impaired portfolio | 3,105 | 157 | 3,262 |
4.2.7. Total impairment losses for the period
The following table shows details of impairment losses and allowances on financial assets and contingent risks and commitments, as well as derecognition of losses previously recognized in asset write-offs recorded directly in the income statement in 2012 and 2011.
(Million euros)
| Items | 2012 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|
| Financial assets | 7,980 | 4,226 |
| Of which: |
|
|
| Recovery of written-off assets | 337 | 327 |
| Contingent exposure and commitments [recoveries (–)] | 61 | -6 |
| TOTAL IMPAIRMENT LOSSES | 8,041 | 4,220 |

