Macroeconomic environment
Economic growth, in general, has been stronger than expected and inflation has stopped its downward trend in recent months. Although restrictive monetary conditions continue to affect the economy through traditional channels, their effects on the dynamics of activity and prices have been partially offset by factors such as the expansionary tone of fiscal policy, the dynamism of the services sector and the still high liquidity.
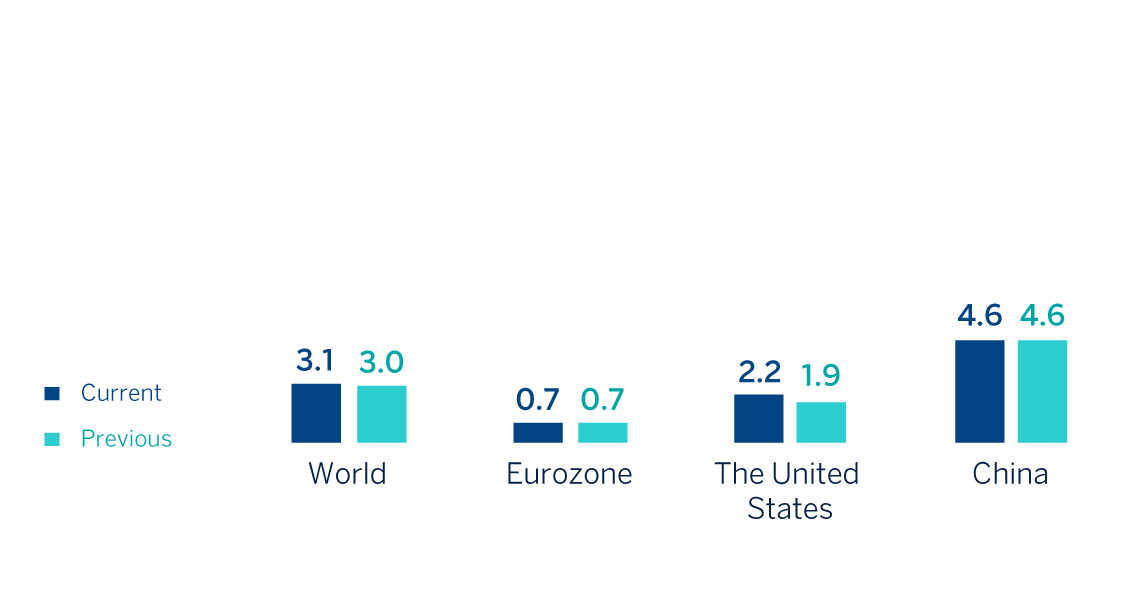
Despite the recent resilience, according to BBVA Research, it is most likely that further moderation in demand paves the way for relatively low global GDP growth and a slowdown in inflation from its current levels over the coming months. Specifically, global growth would reduce from 3.3% in 2023 to 3.1% in 2024, a sightly higher forecast than previous one (+3.0%). In the United States, growth is expected to continue soften, but better than expected data in recent months supports an upward revision of the GDP growth forecast for 2024 to 2.2%, 30 basis points above the previous forecast and 30 basis points below the growth recorded in 2023. In the Eurozone, the growth forecast for 2024 remains unchanged at 0.7%; activity would continue to recover gradually after remaining practically stagnant for much of 2023, when GDP grew just 0.5%. In China, despite the dynamism of the first months of the year, a series of structural factors are expected to continue to weigh negatively and GDP is expected to grow 4.6% in 2024 with no change compared to the previous forecast and below the growth observed in 2023 (+5.2%).
In this context of moderate growth and prospects for a further slowdown of inflation, the ECB has decided to cut its interest rates by 25 basis points in June, to 3.75% of deposit facility rates, and it is expected that the Fed will begin soon its cycle of easing monetary conditions. Benchmark interest rates would be reduced, according to BBVA Research forecasts, to around 5.0% in the United States and 3.25% in the Eurozone, after two cuts of 25 basis points in each geographic area during the second half of 2024. Interest rates are expected to continue falling throughout 2025. However, they are expected to remain relatively high, above the levels before the coronavirus pandemic, due to potential inflationary pressures caused by the geopolitical factors, such as the war in Ukraine and the armed conflict in Middle East, and to other factors like protectionist policies, an expansionary fiscal stance and climatic shocks. Indeed, these factors, as well as the current political context in the United States and Europe, increase the uncertainty about the evolution of the global economy and the risk of having a higher inflation and interest rates than expected as of the date of publication of this report.
GDP GROWTH ESTIMATES IN 2024
(PERCENTAGE. YEAR-ON-YEAR VARIATION)
Source: BBVA Research estimates.